Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) technology is crucial to modern data storage and protection systems.
With the growing demand for network-attached storage (NAS), it’s increasingly important for individuals and businesses to understand the various RAID levels and best RAID for nas or home use.
RAID is a data storage technology that uses multiple NAS hard drives to store data to protect against data loss in the event of a drive failure.
There are several different RAID levels, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
We’ll cover best practices for setting up a RAID Levels for Synology NAS, common issues and challenges you may face, and how to troubleshoot them.
As a general rule of thumb, different RAID setups depend on your need. If you are a small business owner, using RAID 0 or 1 is recommended as it is cost-effective and requires less management while offering high read/write speed.
Whether you’re a professional IT administrator, a small business owner, or an individual looking to protect your valuable data, this blog post will provide the information you need to make informed decisions about your Home NAS RAID setup.
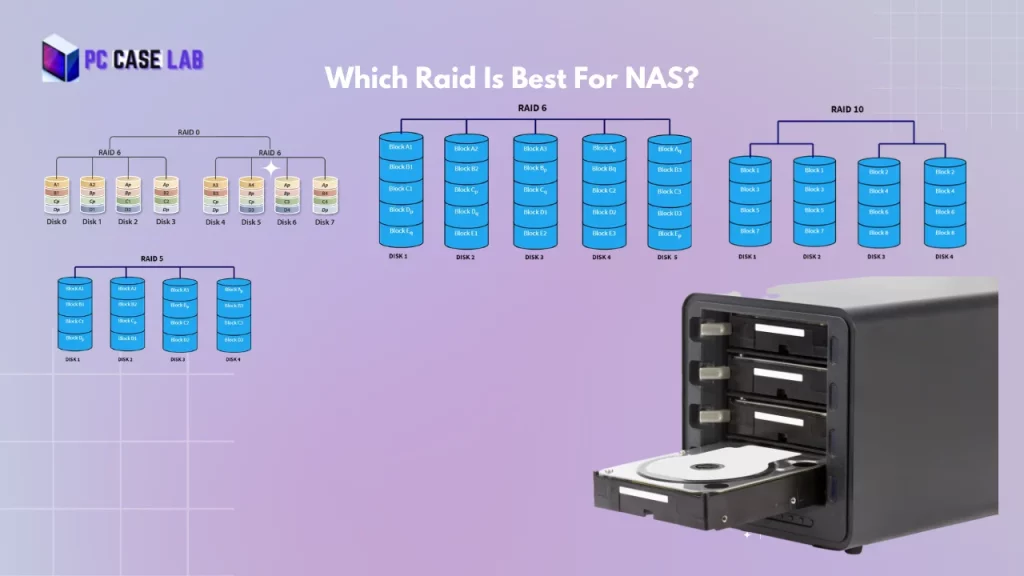
RAID 0 Vs Raid 1 Vs Raid 5 Vs Raid 6 Vs Raid 10 Vs Raid 60
| RAID Levels | Minimum Drives Required | Key Features | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | 2 | Striping (data is split across multiple disks) | Improved performance, but no redundancy |
| RAID 1 | 2 | Mirroring (data is duplicated across multiple disks) | High data redundancy, but limited capacity and no performance improvement |
| RAID 5 | 3 | Striping with parity (data is split and redundant information is stored across multiple disks) | Good data redundancy and some performance improvement, but can suffer from slow write speeds |
| RAID 6 | 4 | Striping with double parity (data is split and two sets of redundant information are stored across multiple disks) | Improved data redundancy over RAID 5, but reduced performance due to increased overhead |
| RAID 10 | 4 | Mirroring and striping (data is duplicated and split across multiple disks) | High data redundancy and good performance, but limited capacity and high cost |
| RAID 60 | 8 | Double parity and striping (data is split and two sets of redundant information are stored across multiple disk groups) | Improved data redundancy and performance over RAID 6, but high cost |
What Is RAID?

RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks and is a data storage technology that utilizes multiple NAS hard drives to store data more efficiently.
The primary benefit of RAID is increased performance and improved reliability since it allows for redundant copies of the same data stored across multiple disks.
But to set up a RAID , you need a good NAS case according to your needs.
RAID levels are the various configurations that define how data is stored across multiple disks. Each level has advantages and disadvantages, and several popular levels exist, such as RAID 0, RAID 01, RAID 05, RAID 06, and RAID 010.
RAID can benefit businesses and individuals, offering improved performance, data protection, and cost savings.
However, it’s important to understand the different RAID levels to choose the best one for your needs.
Types of RAIDs

There are several different RAID levels, each offering its unique benefits and drawbacks. For example, RAID 0 offers high performance but does not provide any data protection; on the other hand, RAID 05 offers a good balance between performance and data protection.
Different popular types of RAIDs include RAID 010, ideal for large storage systems that require high read/write speeds and redundancy, and RAID 06, which provides extra redundancy in case of hard drive failure.
It’s important to understand the differences between these various types of Raids to choose the best one for your specific needs.
Factors such as how much data you need to store, how many drives baysyou have available, and what type of backup requirements you have should all be considered when deciding on a RAID level.
RAID 0 – Best Raid For Video Editing Or Gaming Use
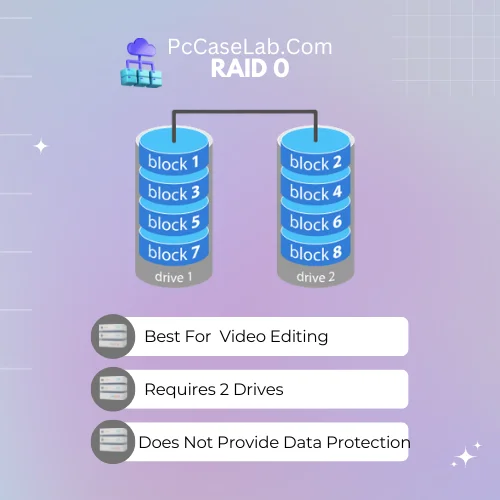
RAID 0 is best in providing enhanced read and write performance, as well as increased storage capacity. It utilises data striping, an efficient data distribution method, to split the data across multiple drives.
This results in a higher bandwidth for data transfers and increases disk input/output operations per second (IOPS). RAID 0 also offers improved recovery capabilities since there are two different drives storing the same data.
However, RAID 0 has its limitations too. Since data is distributed evenly across multiple disks, if one disk fails, you could lose all your data as it would be impossible to recover since it’s spread out over both disks.
Additionally, because of this lack of redundancy, it’s not recommended for mission critical systems unless backed up regularly.
Overall, while RAID 0 provides excellent performance benefits with respect to read/write speeds and storage capacity thanks to its usage of data striping technology, it comes with a tradeoff—the risk of complete data loss if one drive fails makes RAID 0 unsuitable for mission critical systems without regular backups in place.
What Are Raid 0 Best For? – FAQs
While this type of setup can be beneficial for applications that require fast access times, such as video editing or gaming, it should only be used if you are not concerned about losing your data in case of hard drive failure.
| Best In | Weak In |
|---|---|
| Great performance In Read And Write | No Data Protection or Backup |
| Full Storage Capacity Is used | |
| Easy To Implement. | |
| Requires 2 Drives |
RAID 0 (Striping) requires a minimum of 2 drives. The more drives added to RAID 0, the greater the storage capacity and performance. However, it provides no data redundancy and if one drive fails, all data is lost.
No, RAID 0 does not have a backup drive. It is a striping configuration that distributes data across multiple drives for increased performance, but does not provide data redundancy or backup. If a drive fails in a RAID 0 setup, all data will be lost.
RAID 01– Best RAID For Home NAS
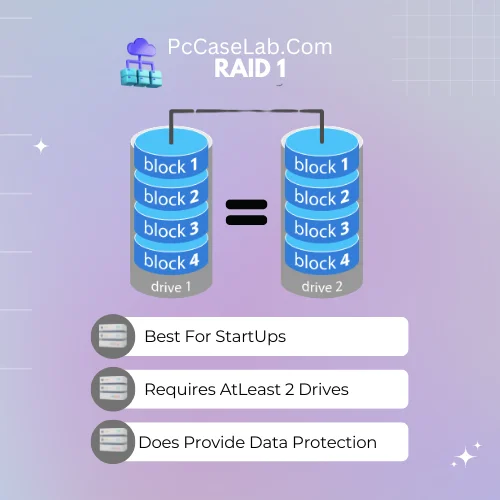
RAID 01, also known as mirroring, is a popular type of RAID configuration that provides excellent performance and good redundancy.
In this setup, two drives bays are configured to store identical copies of the same data. If one disk fails, the other can still be accessed to retrieve your data.
Furthermore, this type of RAID provides a great balance between performance and cost-effectiveness since it requires only two drives instead of three or four, as some other configurations do.
However, it does not provide as much protection against multiple drive failures as higher levels such as RAID 05 or RAID 06. Moreover, RAID 01 requires twice as much storage space since it stores duplicate copies of the same data.
RAID 1 is more suited for applications that require fast access times and good redundancy. It is often used for critical data such as financial records, databases, and is one of the best option for home use or important documents that cannot be easily replaced.
| Best In | Weak In |
|---|---|
| Great performance In Read And Write Compared To Single Drive | Only One Drive Storage Is Used |
| Provides Data Protection And Backup | Does Not Support Hot Swapping. |
| Data Is Mirrored To Other Drive For Backup | |
| Easy Technology |
RAID 1 requires a minimum of 2 drives, providing data mirroring and redundancy in case of drive failure. This ensures data remains available in the event of a drive failure.
No, RAID 1 is not a backup solution. It provides data redundancy by mirroring data across multiple drives, but does not protect against data loss from events such as hardware failure, software errors.
RAID 1 provides data mirroring, but does not provide increased read or write speed compared to a single disk. Instead, RAID 1 offers redundancy and reliability by duplicating data across two or more disks.
RAID 5 – Best For Media Server
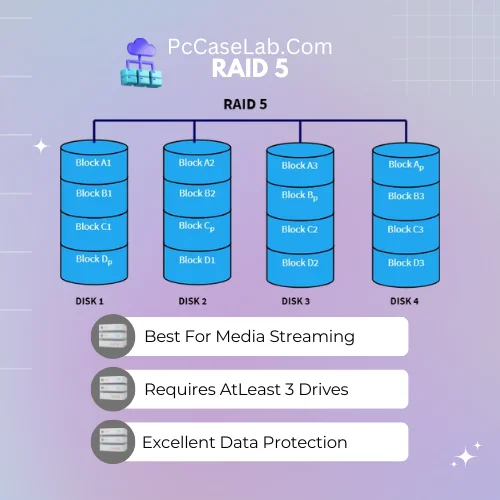
RAID 05 is a popular type of RAID configuration that offers good performance and excellent data protection.
In this setup, at least three disks are used to store data; the first two drives contain identical copies of the same data, while the third store’s parity information which can be used to reconstruct lost or corrupted files in case one of the disks fails.
This type of configuration provides improved performance since it allows for simultaneous read/write operations and redundancy in case of hard drive failure.
However, it does require an extra drive bays for storing parity information which can add to overall costs. Furthermore, RAID 05 also has slower write speeds than some other configurations like RAID 0 or RAID 01 due to its use of parity calculations.
It is best raid for media server that require both read/write performance and data protection, such as file sharing, media streaming, or online backup services.
| Best In | Weak In |
|---|---|
| Great performance In Read But Slower In Write Speed | Complex Compatibility and Technology |
| Supports Hot Swapping | Does Not Support Hot Swapping. |
Yes, RAID 5 can fail due to hardware failure, data corruption, and human error. However, RAID 5 provides data redundancy, which helps in preventing data loss if one of the drives in the array fails.
Yes, a solid-state drive (SSD) can be used in a RAID 5 configuration. However, it is important to note that SSDs have a limited number of write cycles and using them in a RAID 5 can decrease their lifespan. It is recommended to use high-endurance SSDs for RAID 5 and monitor the RAID regularly to prevent data loss.
RAID 5 requires at least three drives to implement, with one drive being dedicated to parity data, allowing for recovery of data in case of a single drive failure.
RAID 6 – Best For Critical Applications
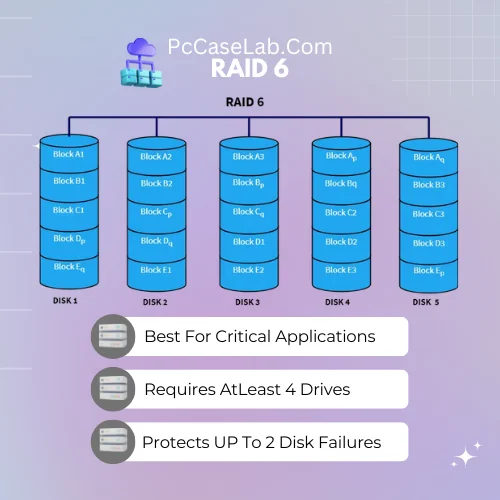
RAID 06 is a type of RAID configuration that offers improved redundancy over RAID 05. In this setup, four or more disks are used to store data and parity information; the first two drives contain identical copies of the same data, while the other two store additional parity bits, which can be used to reconstruct lost or corrupted files in case one or more of the disks fail.
This type of configuration provides good read/write performance and excellent protection against multiple drive failures, making it ideal for mission-critical applications such as online banking systems or databases.
However, it does require an extra pair of drives for storing parity information, which can add to overall costs. Furthermore, RAID 06 also has slower write speeds than some other configurations like RAID 0 or RAID 01 due to its use of parity calculations.
The RAID 6 is best suited for applications that require both read/write performance and data protection. It is also recommended for critical applications like databases or servers where redundancy and reliability are paramount.
| Best In | Weak In |
|---|---|
| Great performance In Read | Slow Write Data Performance |
| RAID 6 Better Protected Then RAID 5. | Complex To Setup |
In a RAID 6, 2 drives can fail without any data loss. The extra parity information stored in the RAID 6 setup allows for recovery from the failure of up to 2 drives.
No, RAID 6 does not increase speed as compared to RAID 5. It provides data redundancy and fault tolerance but requires more processing power for the extra parity calculations, leading to a slower performance.
RAID 10 – Best For Enterprise Solutions
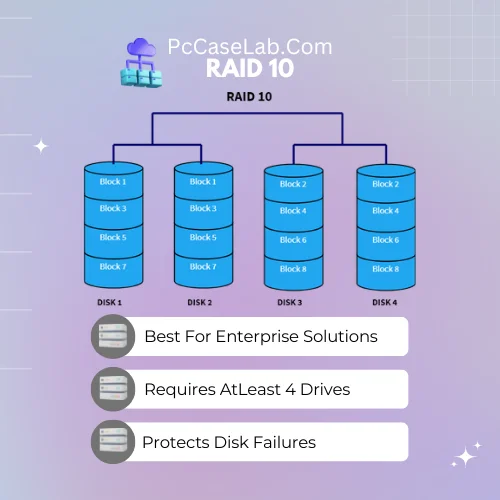
RAID 010, also known as striped mirroring, is a type of RAID configuration that combines the benefits of both striping and mirroring in Synology NAS. In this setup, two or more sets of drives are configured to store identical copies of the same data in a striped fashion; if one drive fails, the other can still be accessed to retrieve your data.
This type of RAID provides excellent performance and redundancy since it stores copies of each file across multiple disks. However, it does require at least four NAS hard drives for optimal performance, which adds to overall costs.
Furthermore, RAID 010 also has slower write speeds than some other configurations like RAID 0 or RAID 05 due to its use of parity calculations.
It is also recommended for mission-critical applications like databases or servers where redundancy and reliability are important.
THE RAID 10 setup can become overkill for small-scale applications or home users and is usually recommended for enterprise solutions.
| Best In | Weak In |
|---|---|
| Fast Rebuild /Backup Time | Half Of The Drives Will Work As A Backup |
RAID 10 requires a minimum of 4 disks and provides both data striping and mirroring for improved data reliability and performance.
Yes, RAID 10 is a fault-tolerant configuration that uses mirroring and striping to provide data redundancy and improved performance. It can withstand up to two disk failures without losing data.
RAID 60 – Best For Commercial Use
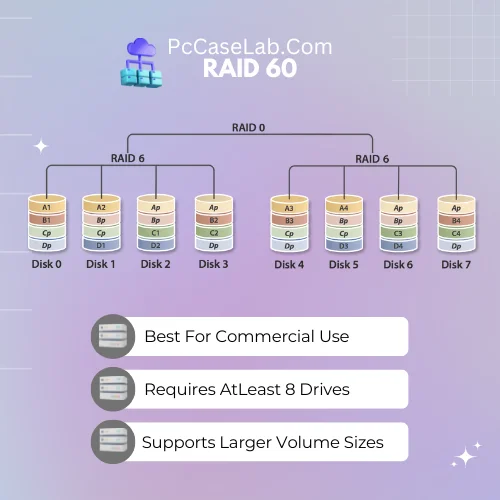
RAID 060 is a type of RAID configuration that combines the benefits of both RAID 05 and RAID 06.
In this setup, at least six disks are used to store data and parity information; the first four drives contain identical copies of the same data, while the other two store additional parity bits, which can be used to reconstruct lost or corrupted files in case one or more of the disks fail.
This type of configuration provides improved read/write performance and excellent protection against multiple drive failures, making it ideal for mission-critical applications such as online banking systems or databases.
However, it does require an extra pair of drives for storing parity information, which can add to overall costs.
RAID 60 requires a minimum of 8 drives, with the exact number depending on the capacity desired. The drives are divided into 2 groups, with one group used for data striping and the other for parity.
RAID 6 is considered to be the safest RAID configuration as it provides data protection through redundancy and uses two sets of parity data distributed across different drives, allowing for continued operation even if two drives fail simultaneously.
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) can potentially be faster than a single SSD as it uses multiple drives to spread data and improve performance. However, it depends on the RAID configuration and the types of SSDs used.
Factors To Consider When Choosing The Best RAID level For Your NAS
When choosing the best RAID level for your NAS, data size, number of drives, backup requirements, and expected performance are factors to consider.
Choosing the right RAID level for your NAS device that meets your needs in terms of performance, data protection, and cost-effectiveness is important.
It is also critical to consider whether you want a hardware or software RAID solution; hardware solutions are better suited for high-performance applications, while software solutions may be more cost-effective.
Furthermore, it is important to properly configure the drives in the array according to your setup and expectations.
In addition, it is important to have a comprehensive data backup strategy in place that will protect your data against unforeseen scenarios such as drive failures or power outages.
Data Size:
The size of your data will determine what type of RAID setup is optimal for you. If you have a large amount of data that needs to be stored, then larger RAID configurations, such as RAID 60 or 70, maybe more suitable since they provide higher levels of redundancy and performance.
Number Of Drives:
Depending on the number of drives in your Synology NAS array, certain RAID configurations may not be possible due to the storage capacity requirements. Furthermore, some types of RAID require an even number of disks for optimal performance and protection.
Backup Requirements:
It is important to consider your backup requirements when choosing a RAID level for your NAS device; if you need frequent backups or are considering online backup services, selecting a higher-level RAID configuration that offers greater redundancy might be best.
Expected Performance:
Depending on your expected performance needs, certain RAID levels may be better suited than others; for instance, if you need high read/write speeds, then it might be best to opt for a lower-level configuration such as RAID 0 or 01.
Budget:
Finally, your budget should also be considered when selecting the best RAID level for your NAS; some configurations may require more drives or hardware controllers, which can add to overall costs.
For cutting down the cost you can your repurpose old computer as NAS server.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Hardware vs. Software RAID solutions
Hardware RAID Solutions
The advantages of hardware RAID solutions include improved performance, better reliability, and easier setup.
They can also provide advanced features such as hot spare disks or support for multiple RAID configurations.
Software RAID Solutions
On the other hand, software RAID solutions are usually cheaper and more flexible since they do not require special hardware controllers; this makes them ideal for small businesses or home users who want to set up a basic NAS system without breaking the bank.
However, software solutions tend to be slower than their hardware counterparts due to overhead associated with parity calculations and data distribution across different drives.
Furthermore, some operating systems may not offer native support for certain software RAID configurations.
Software RAID solutions are best suited for a basic NAS setup with minimal cost and hardware requirements.
However, if you need faster performance and more advanced features, hardware RAID is the way to go.
The Role Of NAS In A RAID Setup.
NAS (Network Attached Storage) is a specialized device designed to provide centralized data access and management over a network.
A NAS system typically consists of one or more hard disks and an operating system such as FreeNAS, OpenFiler, or Windows Storage Server.
When used with RAID technology, a NAS device can provide superior performance, reliability, and scalability compared to traditional single-disk solutions.
Additionally, it can facilitate the sharing of files across different platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux, without additional software.
Furthermore, NAS systems also offer advanced features such as remote access, data replication, and support for multiple RAID configurations.
This makes them ideal for small-to-medium-sized businesses or home users who need an easy-to-use yet powerful solution for their storage needs.
Best Practices For Setting UP a RAID For NAS
When setting up a RAID for NAS, it is important to follow best practices to ensure optimal performance and protection of your data.
- Plan your RAID setup carefully: Before setting up a RAID, it’s important to plan your setup carefully, considering factors such as the number of drives you need, the size of your data, your budget, and your backup requirements. This will help you choose the right RAID level and ensure your NAS device is set up for optimal performance and data protection.
- Use high-quality drives: When setting up a RAID, it’s important to use high-quality drives with a low failure rate to reduce the risk of data loss. It’s also a good idea to use drives from the same manufacturer and with similar specifications to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Use an appropriate RAID level: Your chosen RAID level will depend on your specific needs and requirements. For example, if you need high performance, you may choose RAID 0. If you must protect your data against drive failures, you may choose RAID 5 or RAID 6.
- Use a spare hot drive: A spare hot drive is an extra drive kept in reserve and automatically takes over in the event of a drive failure. This helps to minimize data loss and downtime in the event of a drive failure.
- Regularly monitor your NAS: Regularly monitoring your NAS device is important to ensure it is functioning optimally and detect any potential issues before they become serious problems. This includes monitoring the health of your drives, checking the status of your RAID, and monitoring your backup system.
- Regularly back up your data: Regularly backing up your data is crucial for protecting your data in the event of a drive failure or other disaster. Using a combination of local and off-site backups is a good idea to ensure that your data is protected against data loss.
- Keep firmware up to date: Keeping your NAS firmware up to date can help improve performance and security and fix any bugs or compatibility issues.
Common Issues And Challenges With RAID for NAS
Despite its many benefits, RAID for NAS can also have some challenges. This includes compatibility issues between different drives and operating systems, incorrect drive configurations, and the complexity of setting up a RAID system.
Additionally, there can be performance issues due to high disk utilization or data corruption due to faulty drives or errors in your setup.
To ensure optimal performance and data protection when using RAID for NAS, it’s important to address any potential issues as soon as they arise.
Troubleshooting these problems requires knowledge of the underlying technology and experience dealing with technical issues.
Furthermore, it’s important to regularly monitor your NAS and back up your data to protect against any potential issues.
This will help ensure you can quickly recover from any problems or disasters and minimize the risk of data loss.
It is also important to note that hardware RAID solutions often offer better performance and reliability than software RAID.
However, hardware RAID solutions can be more expensive and require specialized hardware. It’s important to weigh the cost against the benefits of each option when choosing a RAID solution for your NAS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Selecting a best RAID for nas is important because RAID is a great solution for data storage and protection. It offers high performance, reliability, and scalability.
When setting up a RAID system, it’s important to choose the right drives, use an appropriate RAID level, keep your firmware up to date, regularly monitor your NAS, and back up your data. Additionally, hardware solutions often perform better than software solutions but can be more expensive.
When choosing the best RAID level for your NAS setup, it’s important to consider factors such as budget constraints, backup requirements, and performance and data protection needs.
We recommend researching different levels of RAID to find the one that best suits your needs before proceeding. With the right setup and regular maintenance, RAID can be an effective solution for protecting your data.
I am a PC enthusiast with a passion for gaming and all things tech. With years of experience building and customizing PCs, I have become a go-to source for PC case reviews and gaming insights. I am dedicated to researching and writing about the latest trends and developments in the PC gaming industry, with a particular focus on PC cases. From budget-friendly options to high-end builds, I have the expertise to guide you through the process of selecting the perfect case for your needs. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, my in-depth reviews and practical tips will help you make an informed decision.